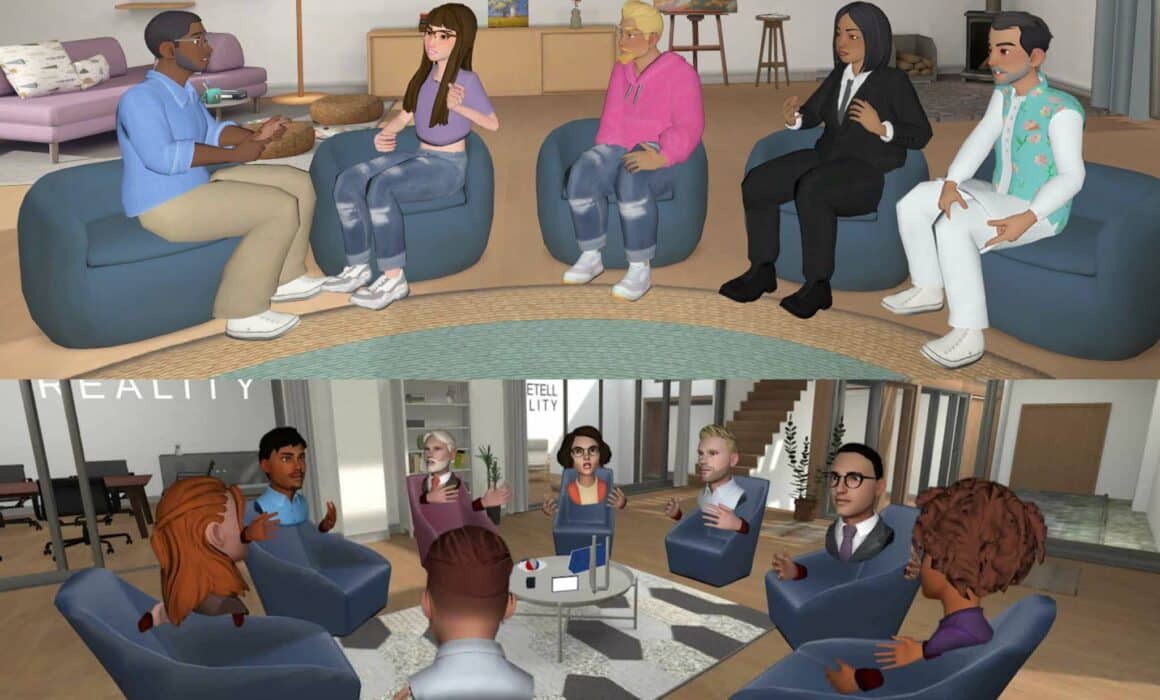
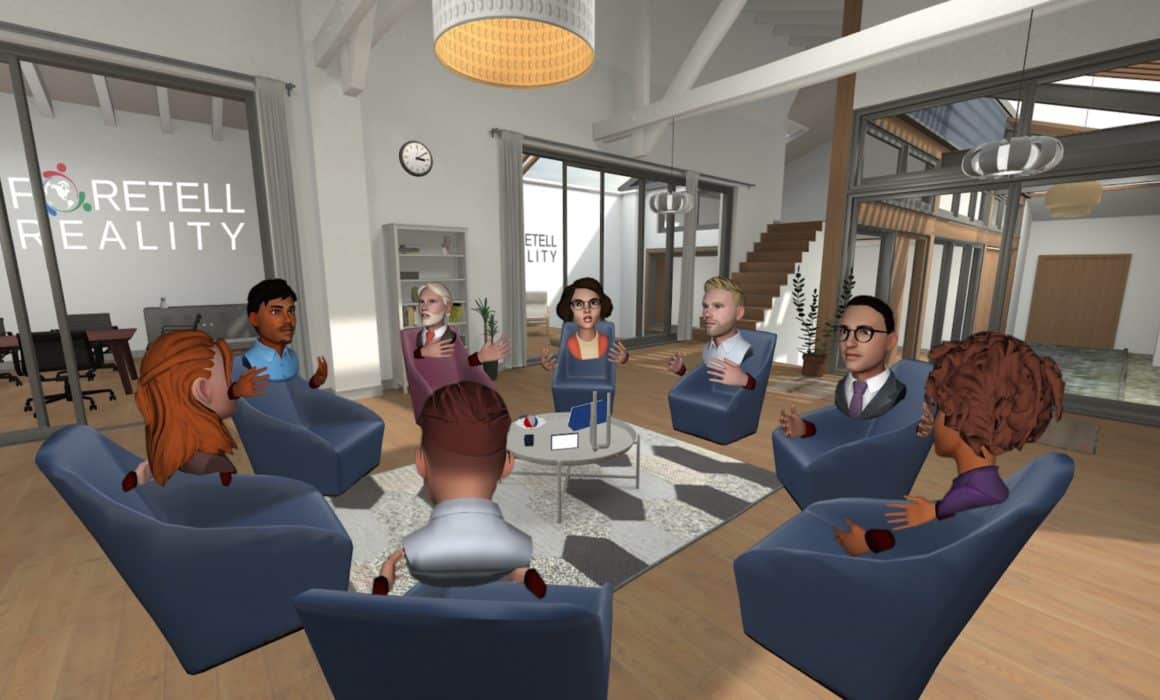
Foretell Reality is proud to announce a major platform upgrade: the launch of full-body avatars across all virtual environments. This enhancement significantly deepens the realism and emotional nuance of virtual interactions by capturing a full range of nonverbal communication, including body language, posture, and gestures. These are key elements in therapy, soft skills training, and role-play-based learning.
The new Meta avatars are seamlessly integrated into Foretell, allowing users to enter sessions with their personalized avatar already configured. With this integration, we’ve received enthusiastic feedback around increased gender inclusivity, a broader variety of clothing options, and customizable accessories that reflect individual identity. When paired with our voice modulation tools, users now have more freedom than ever to express themselves authentically, depending on how they feel on any given day.
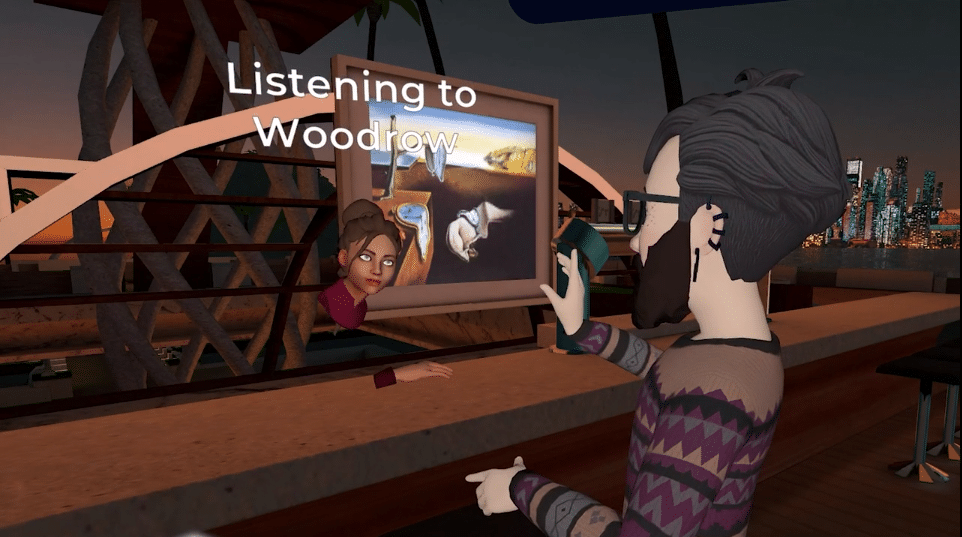
Whether you’re sitting by a virtual campfire, meditating in a tranquil temple, or exploring the dog park, full-body avatars create a stronger sense of presence and connection for both new and experienced users. When combined with our AI Avatar System, this update brings a new level of emotional realism to immersive experiences. It helps users build trust, engage more deeply, and communicate more naturally.
Want to see it in action? Reach out to us today to book a personalized demo!

















Recent Comments